Cell Reports:LZCap® Capped Multivalent mRNA Vaccine Study Shows 100% Immune Protection-1

Recently, the journal Cell Reports published a study jointly conducted
by the Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and other
institutions. The study provides a detailed account of the development of a
multivalent MPOX (monkeypox) mRNA vaccine and its excellent performance
in animal models. The research indicates that the LZCap®-capped multivalent
monkeypox mRNA vaccine can stimulate significant antigen-specific humoral
and cellular immunity, marking another major breakthrough in vaccine
development.
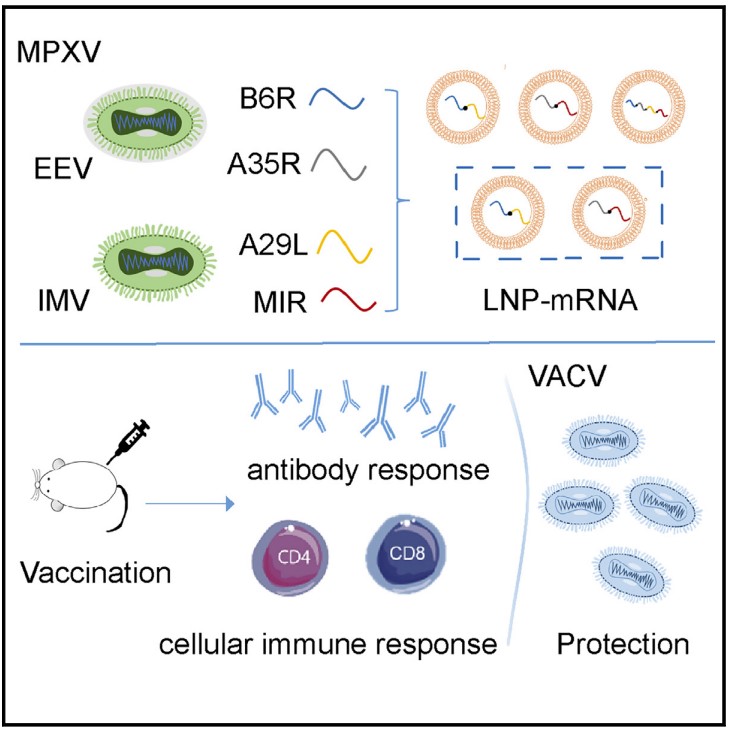
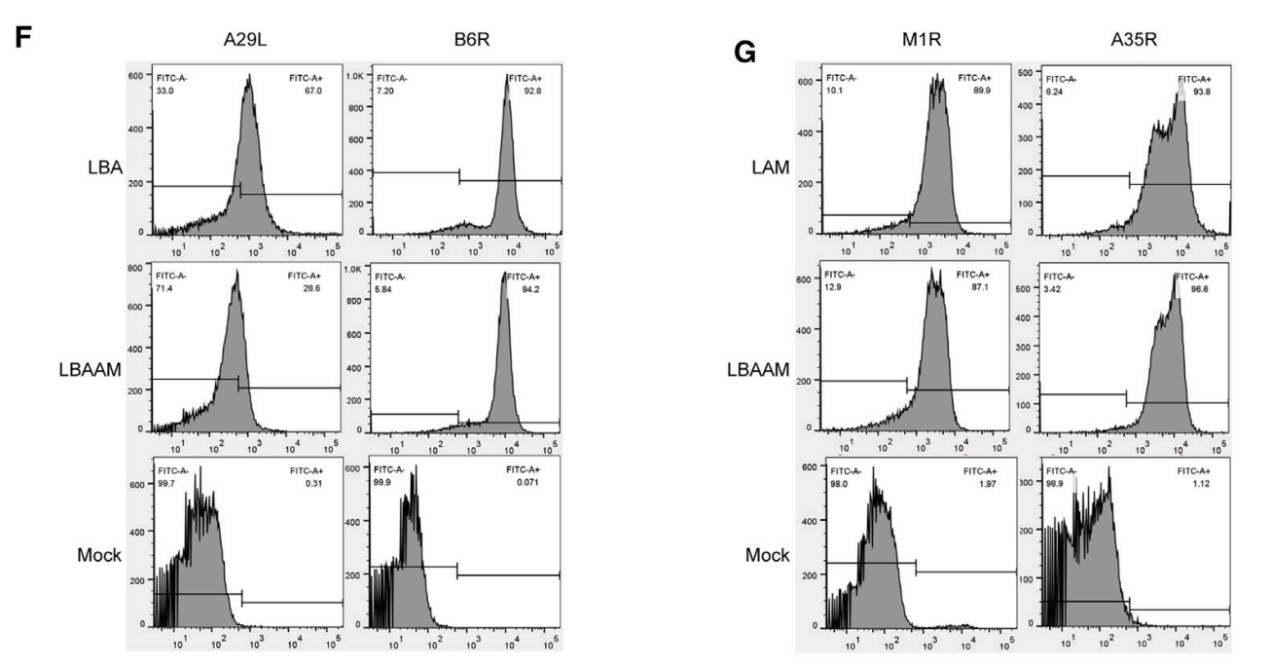
High-Efficiency mRNA Translation
The research team demonstrated that after encapsulation with LNP, the
LZCap® capped multivalent mRNA can be rapidly and efficiently translated
to antigen proteins (B6R, A29L, A35R, and M1R) in the body.
Strong Immune Responses
The LZCap® capped multivalent mRNA vaccine can induce significant
antigen-specific immune responses. The study data shows that after
vaccination with the LZCap® capped MPXV multivalent mRNA vaccine, robust
humoral immune responses induced, and mRNA vaccines also elicited strong
cellular immune responses.
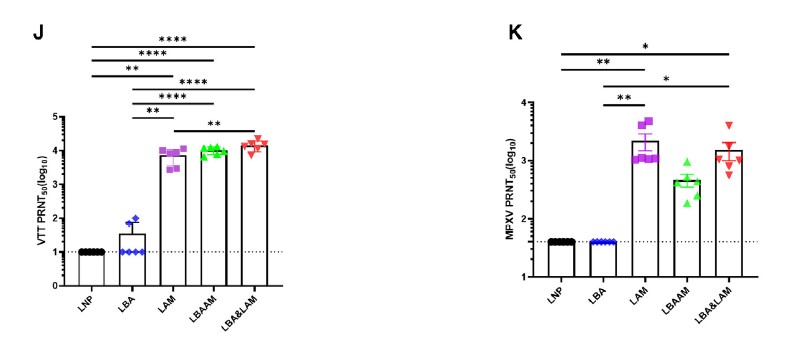
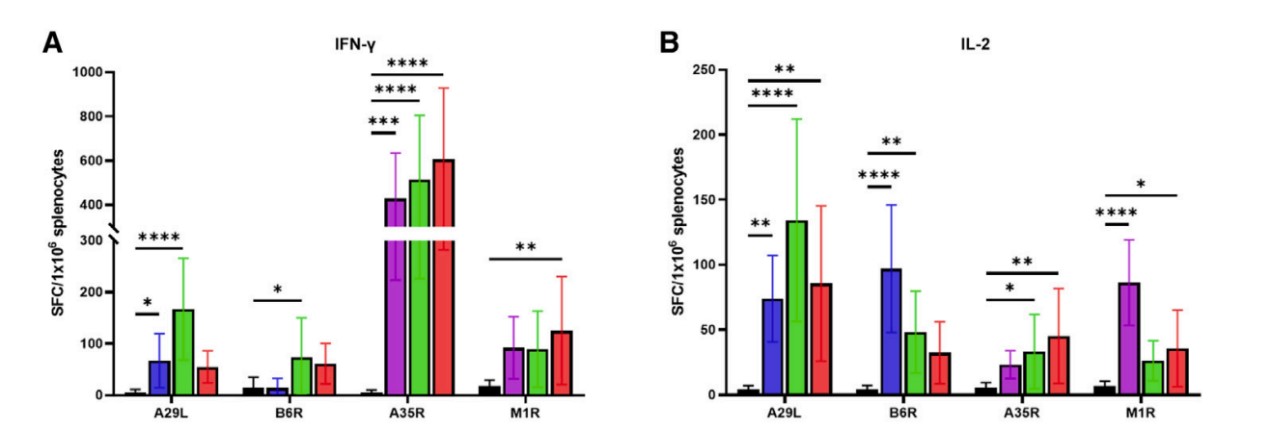
These robust immune responses provide higher protective efficacy for the
vaccine with fewer side effects, showing superior performance when facing
viral challenges.
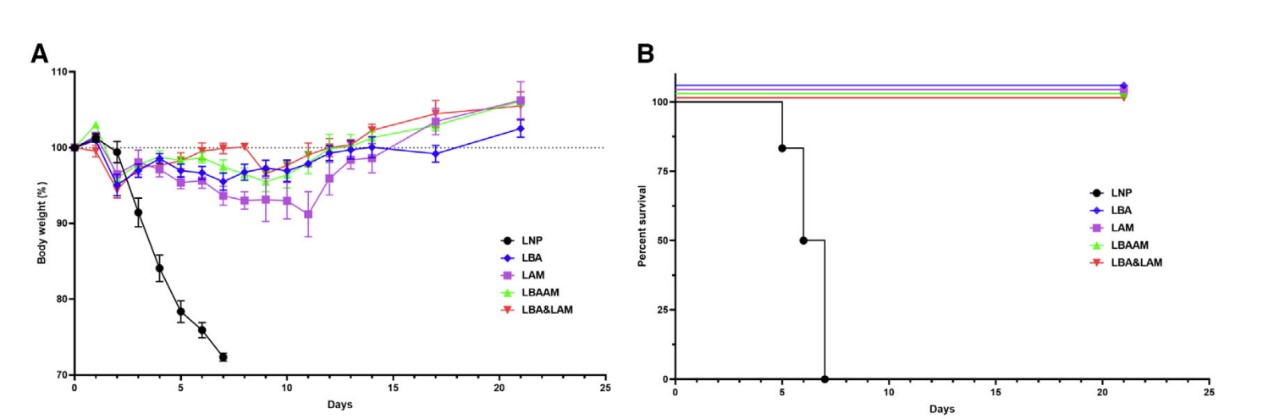
This research presents compelling scientific evidence supporting the
application of LZCap® capping technology in mRNA vaccine development.
As this technology continues to be advanced and implemented, we can
anticipate the emergence of more efficient and safer vaccines, offering
enhanced protection for human health.
The extensive adoption of LZCap® capping technology represents a
substantial advancement in mRNA vaccine development and a significant
breakthrough in biotechnology. We are optimistic that this technology will
contribute to renewed hope and momentum in global public health.
For the full paper, please visit:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38787725/
About LZCap®
Innovative and proprietary mRNA capping agents LZCaps are amenable
for “one-pot”in vitro co-transcriptional capping of mRNA and saRNA.
● High Yield & Capping Efficiency
The mRNA yield is up to 200μg with 1 μg linearized DNA template per
standard IVT reaction with LZCap®AG(3'Acm), about 3-5 times that of ARCA.
LZCap® AG(3'Acm) capping efficiency is over 95%.
● Higher Protein Expression
mRNAs and saRNA with LZCap®AG(3'Acm) show higher protein
expression than mRNAs with marketed Cap1 analog 3'-OMe-7mG trinucleotide
both in vitro and in vivo.
mRNAs with LZCap®AG(3'Acm) show improved stability towards decapping
enzyme compared to those with marketed Cap1 analog.
LZCap®AG(3'Acm) moiety shows higher affinity towards eIF4E complex than
that of marketed Cap1 analog.
● Low cost
Highly efficient LZCap® and streamline of the process control can
significantly reduce the cost of mRNA production.
Supply of high purity LZCap® (>97%) and other triphosphates (>99%) in
a GMP facility with hundreds kilogram capacity at a cost-effective price.
● Safety Profile
mRNAs with LZCap®AG(3'Acm) show low innate immunogenicity.
3'-Acm-7mGTP does not inhibit nor is a substrate of human RNA and
human DNA polymerases. And no genotoxicity was observed in the Ames test.
No cytotoxicity was observed with the 3'-Acm-7mG nucleoside in multiple
cell lines.